|
|
|||
PI: Yang CaiMembers: Orphir Tanz, Rafael de M. Franco
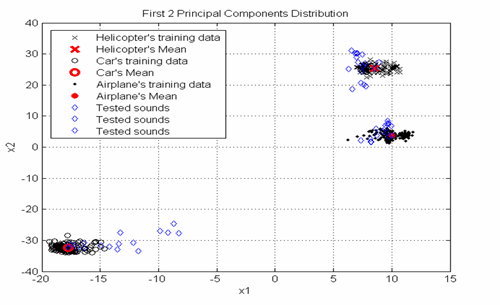
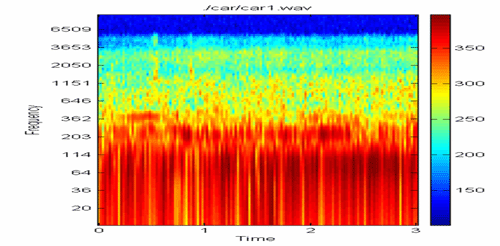
GoalsIndoor wireless sensor self-positioning has been a challenging task. With growing sensor webs, real-time wireless device self-positioning becomes valuable for locating and tracking wireless users. The project is designed to enable an affordable 802.11 RSSI-based positioning technology. We also hope to demonstrate the capability with existing facilities in CMU Andrew wireless network. In addition, we want to demonstrate the privacy technologies. ApproachWe apply multiple filters to estimate the positions of the wireless devices based on the RSSI received from access points in the building. Physical constraints are considered as additional filters.
ResultsThe first prototype CMUSky was built in 2003. In 2006, we rebuild the system with a lighter architecture and a new positioning algorithm. See the live demo at www.cmu.edu/vis.
Applications
ReferenceTanz, O, etc, “Wireless local network positioning”, in Yang Cai (ed), Ambient Intelligence for Scientific Discovery, Lecture Note in Artificial Intelligence, LNAI 3345, Springer, Feb., 2005. |